A Beginner’s Guide to Structural Engineering for Industrial Projects
Structural engineering is a vital discipline in industrial projects, ensuring that buildings and infrastructures are not only functional but also safe, efficient, and durable. Whether it’s a manufacturing plant, refinery, or warehouse, structural engineering forms the foundation of successful industrial developments. This beginner’s guide introduces you to the essentials of structural engineering in industrial contexts.
1. What is Structural Engineering?
Structural engineering is a specialized branch of civil engineering focused on designing and analyzing structures to ensure they can withstand various forces and loads. It involves:
Material Selection: Choosing materials like steel, concrete, or composites based on project needs.
Load Analysis: Calculating the forces acting on a structure, such as weight, wind, seismic activity, and operational loads.
Design Optimization: Creating cost-effective and sustainable designs that meet project goals.
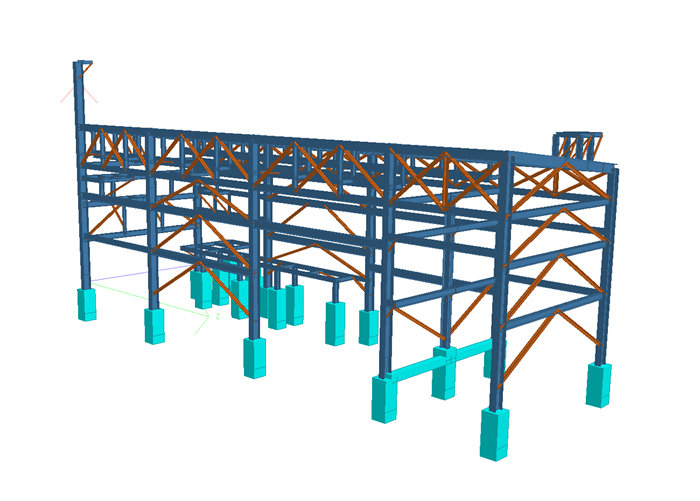
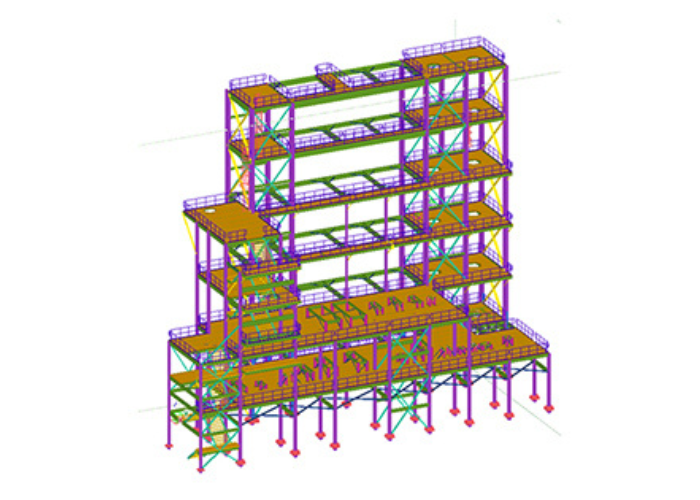
2. Key Elements of Structural Engineering in Industrial Projects
Industrial projects differ significantly from residential or commercial construction due to their complexity and specific requirements. Here are some core aspects:
Foundations: Industrial structures require robust foundations to support heavy machinery and equipment.
Load-Bearing Systems: These include columns, beams, and trusses that distribute loads evenly.
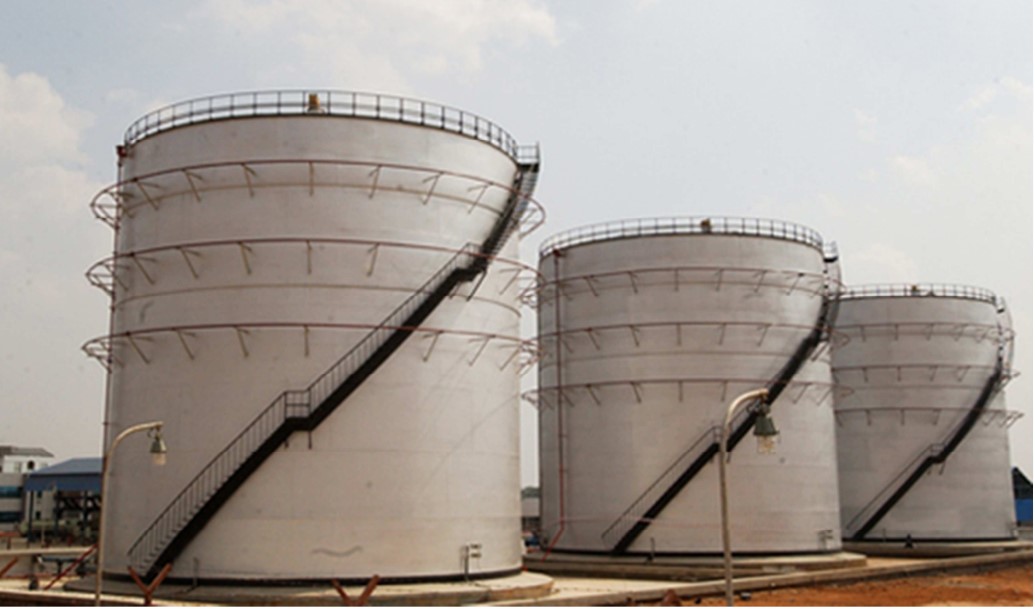
Specialized Structures: Pipe racks, silos, and storage tanks are common in industrial settings.
Dynamic Loads: Consideration of operational vibrations from machinery and equipment.
3. Why is Structural Engineering Important in Industrial Projects?
The role of structural engineering is indispensable for several reasons:
Safety: Ensuring structures can handle extreme conditions and prevent failures.
Efficiency: Designing layouts that optimize space and workflow.
Longevity: Protecting against wear and tear through innovative designs and durable materials.
Compliance: Meeting stringent industry standards and regulations.
4. Phases of Structural Engineering in Industrial Projects
Understanding the workflow helps appreciate the discipline’s complexity:
Conceptual Design: Initial planning based on project requirements and site conditions.
Detailed Analysis: Using software like STAAD.Pro or SAP2000 to calculate loads and stresses.
Material Selection: Choosing materials based on cost, strength, and environmental impact.
Construction Documentation: Preparing detailed drawings and specifications for builders.
On-Site Supervision: Ensuring the construction aligns with the design.
5. Tools and Technologies Used in Structural Engineering
Modern structural engineering relies on advanced tools to ensure precision:
Building Information Modeling (BIM): Enhances collaboration and accuracy in design.
Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Simulates how structures respond to real-world forces.
3D CAD Software: Creates detailed structural models.
Drones and Scanners: Used for surveying and monitoring construction sites.
6. Challenges in Structural Engineering for Industrial Projects
Structural engineers face unique challenges in industrial settings:
Complex Loads: Managing dynamic and heavy loads from machinery.
Environmental Factors: Designing for seismic zones, high winds, or extreme temperatures.
Time and Budget Constraints: Balancing project deadlines and costs with quality.
Sustainability: Incorporating eco-friendly practices without compromising functionality.